Introduction
Peanut butter is a staple food enjoyed by millions around the world. Its rich, creamy texture and nutty flavor make it a versatile ingredient that can be used in a wide range of dishes, from breakfast to snacks and even savory meals. Whether spread on toast, blended into smoothies, or incorporated into sauces and baked goods, peanut butter has become a household favorite. This article explores the history, production, varieties, nutritional value, and versatility of peanut butter.
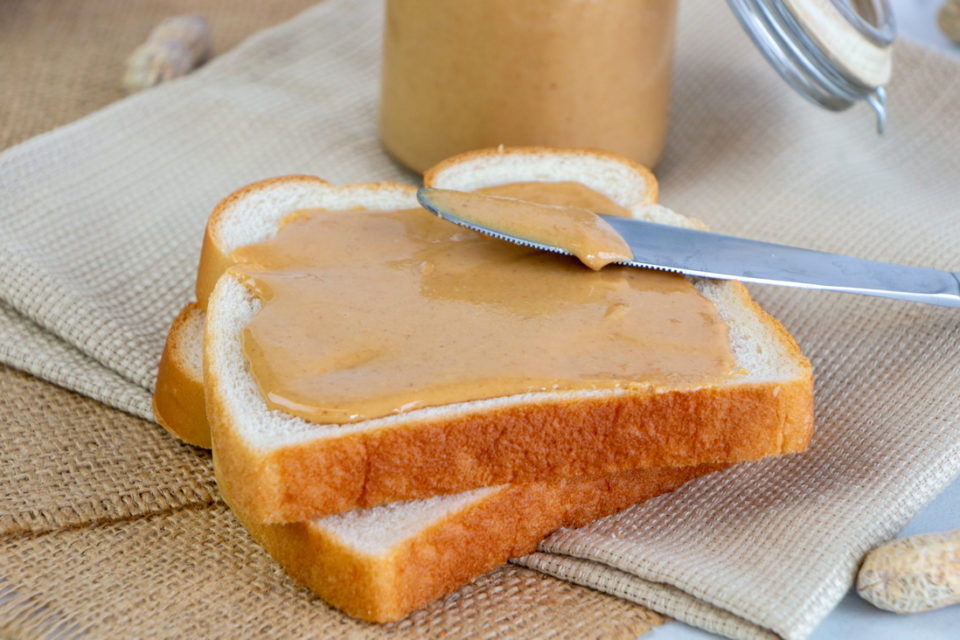

The History of Peanut Butter
Peanut butter has a fascinating history, tracing back to ancient civilizations. Although peanuts originated in South America, it was not until the 19th century that peanut butter became popular in the United States. Early versions of peanut butter were made by grinding peanuts into a paste, but the modern peanut butter we know today was popularized by Dr. John Harvey Kellogg in the late 1800s, who used it as a protein substitute for people with poor teeth. Peanut butter continued to evolve, becoming a household staple and being mass-produced in the early 20th century. Over time, it gained global popularity, especially in North America, where it is a beloved ingredient in many dishes.
The Process of Making Peanut Butter
The production of peanut butter is a straightforward yet precise process. The main ingredients include roasted peanuts, oil, salt, and sometimes sugar. To make peanut butter, peanuts are first roasted, then ground into a paste. The texture of the paste depends on the type of peanut butter being made, which is smooth or crunchy. Smooth peanut butter is created by grinding peanuts until they become a silky, uniform consistency, while crunchy peanut butter includes small, chopped pieces of peanuts for added texture.
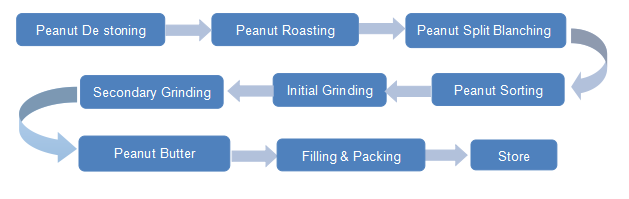
Different Types of Peanut Butter
Peanut butter comes in several varieties to cater to different tastes and dietary preferences.
1.Creamy Peanut Butter: This variety is smooth and easy to spread, with a uniform texture. It is the most commonly available type and is favored for its consistency, making it ideal for sandwiches, smoothies, and desserts.
2.Crunchy Peanut Butter: This variety contains small, chopped pieces of peanuts, giving it a textured, crunchy consistency. It’s perfect for those who enjoy a bit more bite in their peanut butter, adding extra flavor and crunch to sandwiches, snacks, and baking recipes.
3.Natural Peanut Butter: Made from just peanuts and sometimes a pinch of salt, natural peanut butter is free from added sugars, preservatives, and artificial oils. While it may require stirring due to oil separation, it offers a pure and wholesome taste that appeals to health-conscious consumers.
4.Flavored Peanut Butter: Flavored peanut butter comes in various creative varieties, such as chocolate, honey, or cinnamon. These options add a fun twist to the classic peanut butter flavor, making them popular for spreading on toast or adding to desserts for an extra burst of flavor.
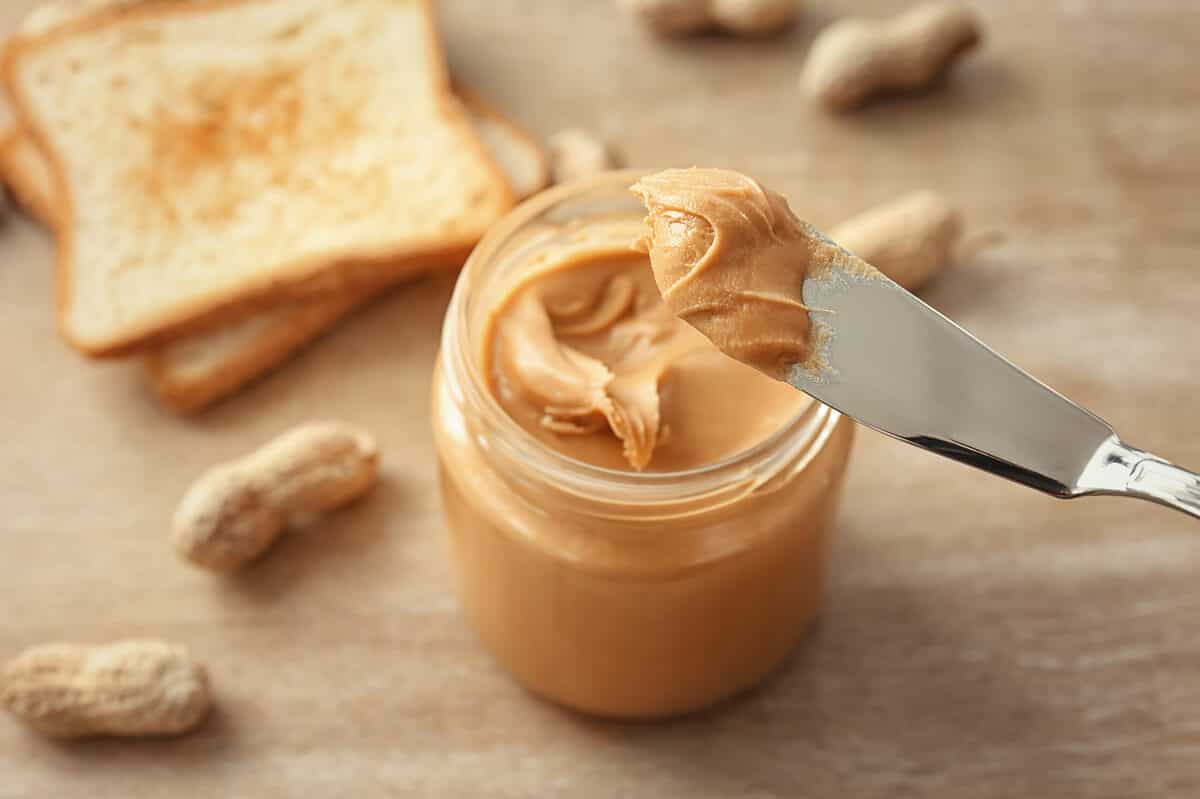


The Nutritional Value of Peanut Butter
Peanut butter is a nutrient-dense food that provides a rich source of protein, healthy fats, and essential vitamins and minerals. It is particularly high in unsaturated fats, which are beneficial for heart health, and is a great option for those looking to increase their protein intake, especially in plant-based diets. Additionally, peanut butter contains important nutrients like vitamin E, B vitamins, and magnesium. While it offers several health benefits, it’s important to enjoy peanut butter in moderation, as it can also be high in calories and fat, especially in sweetened varieties.
Applications of Peanut Butter
Peanut butter is incredibly versatile and can be used in a variety of ways:
1.Breakfast and Snacks: The classic peanut butter and jelly sandwich is a beloved breakfast option. It can also be spread on toast, mixed into smoothies, or paired with fruits like bananas or apples for a quick and satisfying snack.
2.Baking and Desserts: Peanut butter is a key ingredient in many baked goods, such as cookies, brownies, and cakes. It adds richness and flavor to these treats.
3.Savory Dishes: In many Asian cuisines, peanut butter is used in savory dishes, such as Thai peanut sauce for dipping or as a dressing for salads and stir-fries.
4.Protein Supplement: Peanut butter is popular among fitness enthusiasts as a quick and easy source of protein, often added to shakes or eaten as a snack.


Conclusion
Peanut butter is more than just a delicious spread; it is a versatile and nutritious food with a rich history and numerous applications. Whether you're spreading it on toast, baking with it, or enjoying it as a quick protein boost, peanut butter remains a favorite for many around the world. With the ongoing demand for healthier, more sustainable food options, peanut butter is poised for continued success in the global market.
Contact:
Beijing Shipuller Co., Ltd.
WhatsApp: +86 178 0027 9945
Web: https://www.yumartfood.com/
Post time: Dec-06-2024